Keyword
Cloud Cover: 50%
24 record(s)
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Status
-
The Normalized Difference Water Index algorithm was developed by Gao (19964) being a measure of liquid water molecules in vegetation canopies that interacted with the incoming solar radiation. NDWI is sensitive to changes in liquid water content of vegetation canopies. It is less sensitive to atmospheric effects than NDVI. NDWI does not remove completely the background soil reflectance effects therefore it should be considered as an independent vegetation index. It is complementary to not a substitute for NDVI. The NDWI results from the following equation: NDWI = (IR_factor * near_IR - mir_factor * middle_IR) / (IR_factor * near_IR + mir_factor * middle_IR)
-

Chlorophyll content in the leaf: corresponds to the content of chlorophyll a chlorophyll b and carotenoids per unit of leaf area.
-
The Pigment Specific Simple Ratio (chlorophyll index) algorithm was developed by Blackburn (1998). It investigates the potential of a range of spectral approaches for quantifying pigments at the scale of the whole plant canopy. When applying existing narrow-band pigment indices the PSSR algorithms have the strongest and most linear relationships with canopy concentration per unit area of Chl a (Chlorophyll a) Chl b (Chlorophyll b) and Cars (carotenoids). The PSSRa results from the following equation: PSSRa = (IR_factor * near_IR) / (red_factor * red)
-
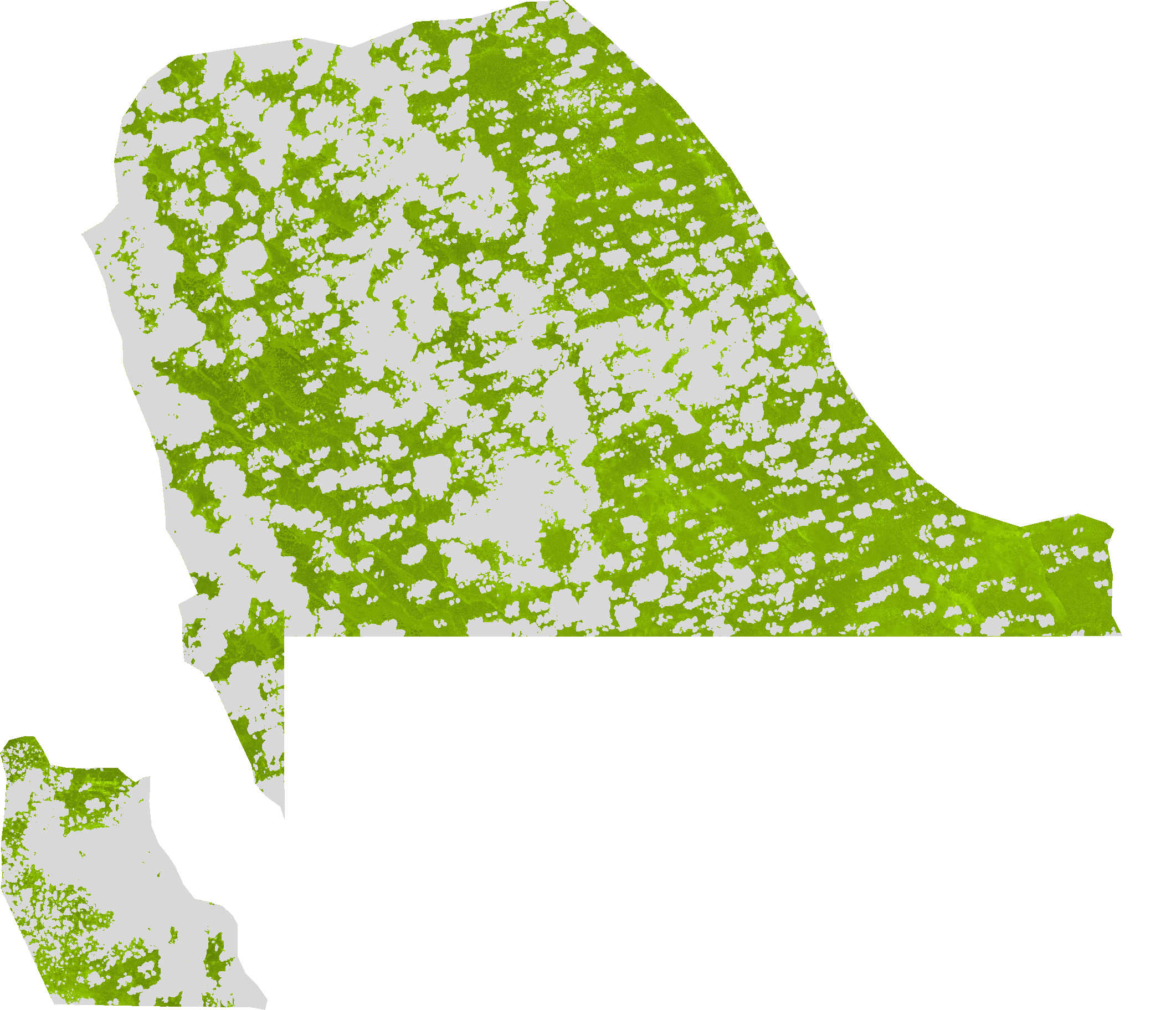

The Normalized Difference Pond Index algorithm was developed by J.P Lacaux et al. (2006).The NDPI makes it possible not only to distinguish small ponds and water bodies (down to 0.01 ha) but also to differentiate vegetation inside ponds from that in their surroundings The NDPI results from the following equation: NDPI = (mir_factor * middle_IR - green_factor * green) / (mir_factor * middle_IR + green_factor * green)
-
The Normalised Difference Turbidity Index (NDTI) quantifies the difference in reflectance between specific spectral bands which correlates with suspended sediment and turbidity levels.
-

The Redness Index algorithm was developed to identify soil colour variations - Pouget et al.(1990). The RI results from the following equation: RI = (red_factor * red * red_factor * red) / (green_factor * green * green_factor * green * green_factor * green)
-
The Normalized Burn Ratio Index (NBR) uses the NIR and SWIR bands to emphasize burned areas while mitigating illumination and atmospheric effects. NBR = (NIR - SWIR) / (NIR+ SWIR)
-

The Weighted Difference Vegetation Index algorithm was introduced by Clevers (1988). This has a relationship to PVI similar to the relationship IPVI has to NDVI. WDVI is a mathematically simpler version of PVI but it has an unrestricted range.Like PVI WDVI is very sensitive to atmospheric variations (Qi et al. 1994). The WDVI results from the following equation: WDVI = (IR_factor * near_IR - g * red_factor * red) where: g is the slope of the soil line.
-
The Red-Edge Inflection Point Index algorithm was developed for applications in biomass and nitrogen (N) uptake measurement/management in heterogeneous fields.- Guyot et al. (1988). Red edge as the inflection point of the strong red absorption to near infrared reflectance includes the information of both crop N and growth status. The reflectance around red edge is sensitive to wide range of crop chlorophyll content N content LAI and biomass (Hatfield et al. 2008 Mutanga and Skidmore 2007 Steele et al. 2008b). The REIP general formula is based on linear four-point interpolation technique and it uses four wavebands (670 700 740 and 780 nm) - Guyot and Baret (1988). The REIP results from the following (Sensor-dependent) equation: REIP = 700 + 40 * ((r670 + r780)/2 - r700) / (r740 - r700) - as general formula or: REIP = 700 + 40 * ( (red1_factor * red1 + IR_factor * near_IR)/2) - red2_factor * red2 ) / (red3_factor * red3 - red2_factor * red2) )
-

MCARI gives a measure of the depth of chlorophyll absorption and is very sensitive to variations in chlorophyll concentrations as well as variations in Leaf Area Index (LAI). MCARI values are not affected by illumination conditions the background reflectance from soil and other non-photosynthetic materials observed.
